SPAmix and SPAmix+ methods
Main features
SPAmix and SPAmix+ are accurate and efficient approaches to associating complex traits (including but not limited to quantitative, binary, time-to-event, ordinal, and longitudinal traits) to single variant.
The two methods use restropective saddlepoint approximation (SPA) approaches and share the below features.
- Model residuals (whose sum is zero) are needed as input. Users can select appropriate statistical models depending on the type of traits in analysis.
- High computational efficiency to analyze large-scale biobank data with millions of individuals
- High accuracy to analyze common, low-frequency, and rare variants, even if the phenotypic distribution (or residual distribution) is highly unbalanced (e.g. case-control imblance in case-control studies).
The two methods are different in terms of
-
SPAmixis designed to analyze an admixture population or multiple populations and can incorporate local ancestry information into analyses. The method is still only valid to analyze unrelated subjects. -
SPAmix+is a scalable, accurate, and universal analysis framework to control for population structure and family relatedness. The method is valid to analyze heterogeneous or admixed populations with falily relatedness.
| Method | Account for population structure | Account for local ancestry | Account for family relatedness | Prospective/Retrospective |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPACox | NO | NO | NO | Prospective |
| SPAmix | YES | YES | NO | Retrospective |
| SPAGRM | NO | NO | YES | Retrospective |
| SPAmix+ | YES | YES | YES | Retrospective |
Workflow of SPAmix
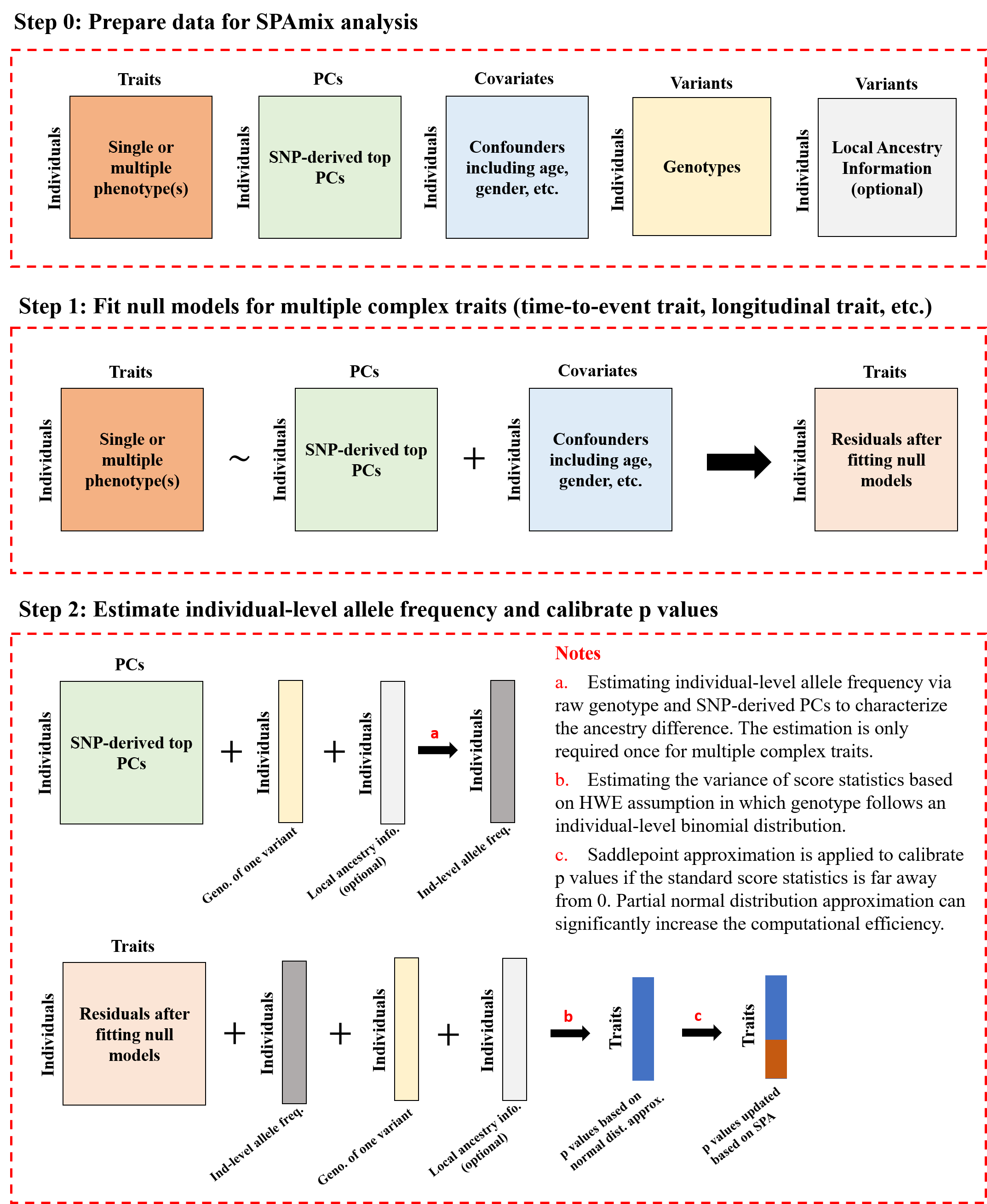
The SPAmix paper and the SPAmix+ paper are two distinct papers
Please note that the SPAmix paper and the SPAmix+ paper are two distinct papers. Unfortunately, although the SPAmix algorithm was completed in 2021, its submission was delayed for some reasons. Consequently, the SPAmix+ algorithm will be presented in a separate paper rather than within the SPAmix paper.
-
SPAmix has been implemented in R package GRAB.
-
The package of SPAmix+ is in preparation.
Important notes about SPAmix in function GRAB.NullModel
-
If the left side of argument
formulais model residual, please specify the argumenttraitType = "Residuals". Otherwise, the argumenttraitTypecan be specified based on the type of trait in analysis. -
For method
SPAmix, the top SNP-derived PC and related information is required in the argumentsformulaandcontrol.
Quick Start-up Guide
The below gives examples to demonstrate the usage of SPAmix.
Step 1. Read in data and fit a null model
library(GRAB)
PhenoFile = system.file("extdata", "simuPHENO.txt", package = "GRAB")
PhenoData = data.table::fread(PhenoFile, header = T)
SPAmix method also support both original trait or model residuals as input. For SPAmix, the confounding factors of SNP-derived PCs are required and should be specified in control.
library(GRAB)
PhenoFile = system.file("extdata", "simuPHENO.txt", package = "GRAB")
PhenoData = data.table::fread(PhenoFile, header = T)
N = nrow(PhenoData)
PhenoData = PhenoData %>% mutate(PC1 = rnorm(N), PC2 = rnorm(N)) # add two PCs
obj.SPAmix = GRAB.NullModel(Surv(SurvTime, SurvEvent)~AGE+GENDER+PC1+PC2, data = PhenoData, subjData = IID, method = "SPAmix", traitType = "time-to-event", control = list(PC_columns = "PC1,PC2"))
The same results can be obtained via using model residuals
obj.coxph = coxph(Surv(SurvTime, SurvEvent)~AGE+GENDER+PC1+PC2, data = PhenoData)
obj.SPAmix = GRAB.NullModel(obj.coxph$residuals~AGE+GENDER+PC1+PC2, data = PhenoData, subjData = IID, method = "SPAmix", traitType = "Residual", control = list(PC_columns = "PC1,PC2"))
Step 2. Conduct genome-wide association studies
For different types of traits and methods, the step 2 is the same as below.
GenoFile = system.file("extdata", "simuPLINK.bed", package = "GRAB")
OutputDir = system.file("results", package = "GRAB")
# step 2 for SPAmix method
OutputFile = paste0(OutputDir, "/Results_SPAmix.txt")
GRAB.Marker(obj.SPAmix, GenoFile = GenoFile, OutputFile = OutputFile)
Citation
-
SPAmix: A scalable, accurate, and universal analysis framework using individual-level allele frequency for large-scale genetic association studies in an admixed population (to be updated).
-
SPAmix+: to be submitted.