SPAGxE+
SPAGxE+ is a scalable and accurate G×E analytical framework that controls for sample relatedness and unbalanced phenotypic distribution.
Introduction of SPAGxE+
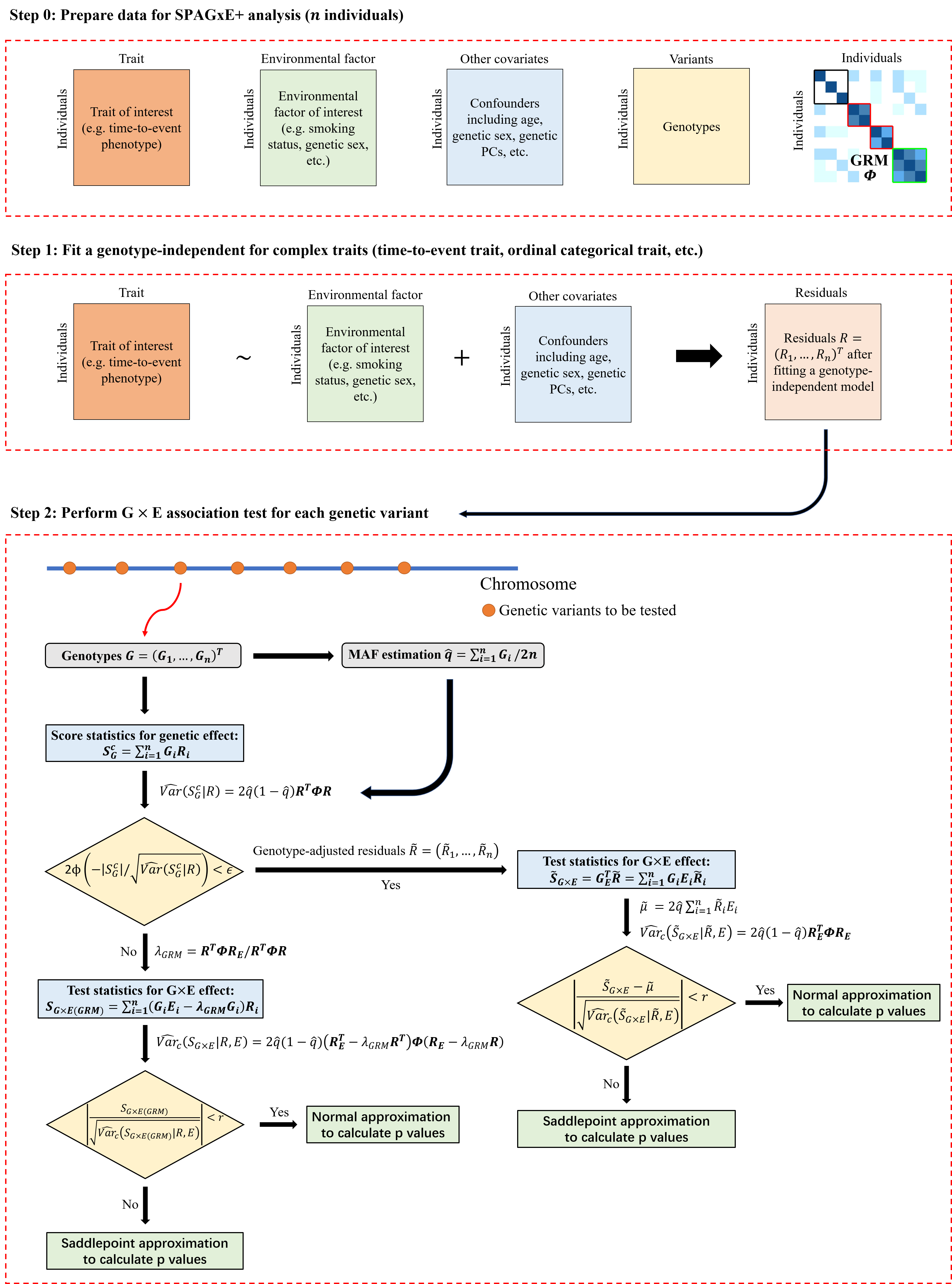
SPAGxE+ is applicable to a wide range of complex traits with intricate structures, including binary, quantitative, time-to-event, ordinal categorical, longitudinal, and other complex traits. The framework involves two main steps:
-
Step 1: SPAGxE+ fits a covariates-only model to calculate model residuals. These covariates include, but are not limited to, confounding factors such as age, sex, SNP-derived principal components (PCs), and environmental factors. The specifics of the model and residuals vary depending on the trait type. Since the covariates-only model is genotype-independent, it only needs to be fitted once across a genome-wide analysis. Incorporating random effects to account for sample relatedness in null model fitting is optional, rather than required.
-
Step 2: SPAGxE+ identifies genetic variants with marginal G×E effects on the trait of interest. First, marginal genetic effects are tested using score statistics. If the marginal genetic effect is not significant, SG×E is used as the test statistic to characterize the marginal G×E effect. If significant, SG×E is updated to genotype-adjusted test statistics. To balance computational efficiency and accuracy, SPAGxE+ employs a hybrid strategy combining normal distribution approximation and SPA to calculate p-values, as used in SPAGxECCT and previous studies such as SAIGE and SPAGE.
Main features of SPAGxE+
Currently, there is still a lack of scalable and accurate gene-environmental interaction analytical frameworks that can control for sample relatedness and be applicable to binary, time-to-event, ordinal categorical, or longitudinal trait analysis. It is usually challenging to detect gene-environmental interaction effects efficiently and accurately while adjusting for sample relateness in a large-scale genome-wide analysis. In GWAS for thousands of phenotypes in large biobanks, most binary traits have substantially fewer cases than controls. Existing methods based on logistic mixed model produce inflated type I errors in the presence of unbalanced case-control ratios.
SPAGxE+ is a scalable and accurate G×E analytical framework that uses saddlepoint approximation to calibrate the null distribution of test statistics while controlling for sample relatedness and case-control imbalance.
- Compared to SPAGxE, a sparse genetic relationship matrix (GRM) is used for characterizing familial structure.
- SPAGxE+ provides accurate p-values even when case-control ratios are extremely unbalanced (e.g. case:control = 1:99).
- SPAGxE+ is applicable to other complex traits including time-to-event, ordinal categorical, and longitudinal traits, and it maintains highly accuracy even when phenotypic distribution is unbalanced.
Quick start-up examples (genotype input using R matrix format)
The following example illustrates how to use SPAGxE+ to analyze a binary trait, with genotype data input provided in the R matrix format.
Step 1. Read in data and fit a genotype-independent model
library(SPAGxECCT)
# load in binary phenotype, genotype, and sparseGRM
data("Phen.mtx.SPAGxEPlus.binary")
data("sparseGRM.SPAGxEPlus")
data("GenoMat.SPAGxEPlus")
Phen.mtx = Phen.mtx.SPAGxEPlus.binary # phenotype data
E = Phen.mtx$E # environmental factor
Cova.mtx = Phen.mtx[,c("Cov1","Cov2")] # Covariate matrix excluding environmental factor
### fit a genotype-independent model for the SPAGxE+ analysis
obj.SPAGxE_Plus_Nullmodel = SPAGxE_Plus_Nullmodel(traits = "binary",
Y ~ Cov1+Cov2+E,family=binomial(link="logit"),
data = Phen.mtx,
pIDs = Phen.mtx$IID,
gIDs = rownames(GenoMat.SPAGxEPlus),
sparseGRM = sparseGRM.SPAGxEPlus,
E = E)
Step 2. Conduct a marker-level association study
# calculate p values
binary.res = SPAGxE_Plus(Geno.mtx = GenoMat.SPAGxEPlus,
E = E,
Phen.mtx = Phen.mtx,
Cova.mtx = Cova.mtx,
obj.SPAGxE_Plus_Nullmodel = obj.SPAGxE_Plus_Nullmodel)
binary.res = as.data.frame(binary.res)
# we recommand using column of 'p.value.spaGxE.plus' as p-values testing for marginal GxE effect
head(binary.res)
Quick start-up examples (genotype input using PLINK file format)
The following example illustrates how to use SPAGxE+ to analyze a binary trait, with genotype data input provided in PLINK file format.
Step 1. Read in data and fit a genotype-independent model
library(SPAGxECCT)
# load in binary phenotype, genotype, and sparseGRM
data("Phen.mtx.SPAGxEPlus.binary")
data("sparseGRM.SPAGxEPlus")
Phen.mtx = Phen.mtx.SPAGxEPlus.binary # phenotype data
E = Phen.mtx$E # environmental factor
Cova.mtx = Phen.mtx[,c("Cov1","Cov2")] # Covariate matrix excluding environmental factor
GenoFile = system.file("", "GenoMat_SPAGxE_Plus.bed", package = "SPAGxECCT") # PLINK format for genotype data
### fit a genotype-independent model for the SPAGxE+ analysis
obj.SPAGxE_Plus_Nullmodel = SPAGxE_Plus_Nullmodel(traits = "binary",
Y ~ Cov1+Cov2+E,family=binomial(link="logit"),
data = Phen.mtx,
pIDs = Phen.mtx$IID,
gIDs = rownames(GenoMat.SPAGxEPlus),
sparseGRM = sparseGRM.SPAGxEPlus,
E = E)
Step 2. Conduct a marker-level association study
# calculate p values
binary.res = SPAGxE_Plus(GenoFile = GenoFile,
E = E,
Phen.mtx = Phen.mtx,
Cova.mtx = Cova.mtx,
obj.SPAGxE_Plus_Nullmodel = obj.SPAGxE_Plus_Nullmodel)
binary.res = as.data.frame(binary.res)
# we recommand using column of 'p.value.spaGxE.plus' as p-values testing for marginal GxE effect
head(binary.res)
Quick start-up examples (genotype input using BGEN file format)
The following example illustrates how to use SPAGxE+ to analyze a binary trait, with genotype data input provided in BGEN file format.
Step 1. Read in data and fit a genotype-independent model
library(SPAGxECCT)
# load in binary phenotype, genotype, and sparseGRM
data("Phen.mtx.SPAGxEPlus.binary")
data("sparseGRM.SPAGxEPlus")
Phen.mtx = Phen.mtx.SPAGxEPlus.binary # phenotype data
E = Phen.mtx$E # environmental factor
Cova.mtx = Phen.mtx[,c("Cov1","Cov2")] # Covariate matrix excluding environmental factor
# BGEN format for genotype data
GenoFile = system.file("", "GenoMat_SPAGxE_Plus.bgen", package = "SPAGxECCT")
GenoFileIndex = c(system.file("", "GenoMat_SPAGxE_Plus.bgen.bgi", package = "SPAGxECCT"),
system.file("", "GenoMat_SPAGxE_Plus.sample", package = "SPAGxECCT"))
### fit a genotype-independent model for the SPAGxE+ analysis
obj.SPAGxE_Plus_Nullmodel = SPAGxE_Plus_Nullmodel(traits = "binary",
Y ~ Cov1+Cov2+E,family=binomial(link="logit"),
data = Phen.mtx,
pIDs = Phen.mtx$IID,
gIDs = rownames(GenoMat.SPAGxEPlus),
sparseGRM = sparseGRM.SPAGxEPlus,
E = E)
Step 2. Conduct a marker-level association study
# calculate p values
binary.res = SPAGxE_Plus(GenoFile = GenoFile,
GenoFileIndex = GenoFileIndex,
E = E,
Phen.mtx = Phen.mtx,
Cova.mtx = Cova.mtx,
obj.SPAGxE_Plus_Nullmodel = obj.SPAGxE_Plus_Nullmodel)
binary.res = as.data.frame(binary.res)
# we recommand using column of 'p.value.spaGxE.plus' as p-values testing for marginal GxE effect
head(binary.res)
Citation
- A scalable and accurate framework for large-scale genome-wide gene-environment interaction analysis and its application to time-to-event and ordinal categorical traits (to be updated).